Accelerated Innovation

The 4th Industrial Revolution is characterised by addressing the many challenges facing the manufacturing industry, with a major focus on optimizing production and streamlining processes. Advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence-enabled solutions, IoT and industrial internet of things (IIoT), cybersecurity, robotics, artificial vision, nanotech, digital-twin, augmented or virtual reality (AR/VR) and additive manufacturing enable companies to take on these challenges.
AI - Artificial Intelligence
AI can be found in so many areas of business nowadays, but is only recently being implemented in the manufacturing industry and onto factory floors. AI is used to gather data, organize that data into useful information and learn from it to implement more intelligent decision making..
AI is used in big data analytics and can be implemented in ways like predictive maintenance in advanced manufacturing. Predicting maintenance of large, high volume machines means more insight and less downtime. AI is now being used in the health industry to help diagnose patients faster. AI is starting to be used in the food sector for retail analytics, to determine trends in sales, footfall, product stock, etc. There is great potential for AI-enabled solutions in more areas across all industries and what we’ve seen already is just the tip of the iceberg.
In particular, network camera deployments are increasingly using analytics to enhance the capabilities of surveillance systems. The basic analytics of motion detection, line crossing and object removal have now been expanded to include facial recognition, heat mapping, people counting and many others.


IoT, IIoT and IoE
IoT, or internet of things when applied to manufacturing has now become the industrial internet of things or IIoT.
What we will see in the years ahead is the internet of everything (IoE).
IIoT allows sensors and adapters to be integrated onto shop floors and all stages of production. IoE combines real-time data from all areas of the factories and facilities, machine or artificial intelligence and human insight, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Robotics and Machine Vision
The use of robotics has long been a method to increase productivity and to improve automation on a large scale. The trends that we see ahead will center around the use of robotics and cobot (collaborative human-robot) solutions in more and more areas.
Additionally, we predict an increase in the implementation of machine or computer vision to improve the accuracy of classification, verification and quality control along assembly lines for example.
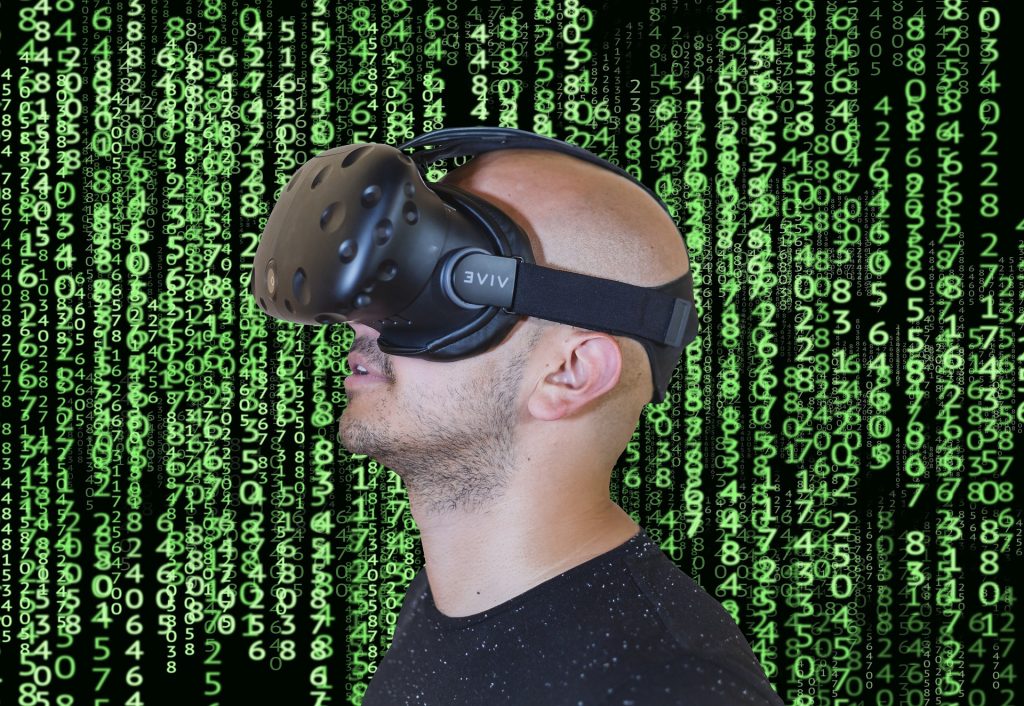


AR, VR and XR
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) as well as what is being called Extended Reality (XR) are other trends allowing the industry to advance into the future. We’ve already seen AR/VR used in Research & Development, high-risk virtual training and even in the production processes. Just like the increased use of robotics, the nature of human-machine interactions in manufacturing is trending toward more machine-enabled workers and XR solutions allow companies to make those moves.
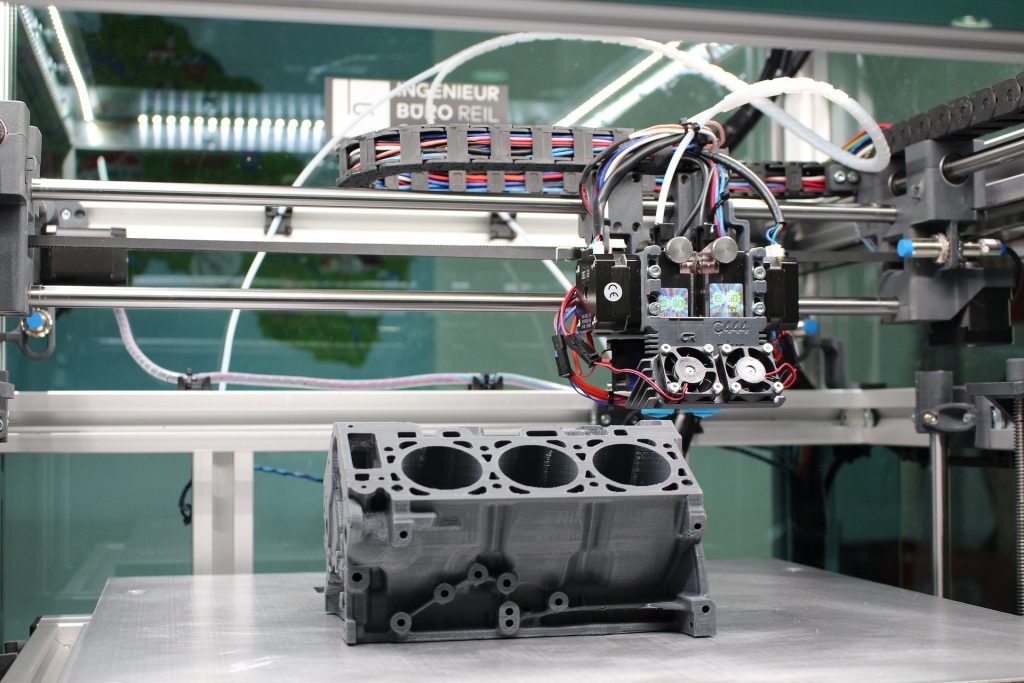
Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing started out as a prototyping method but has steadily become an important part of the production process. Using Industrial 3D printers and industry-specific additives, allows companies to create low-cost products in a short period of time, with better design and faster than before.

Cloud Computing and Blockchain
There is an increased use of cloud computing and distributed systems like blockchain across the Energy, Food, Health and Advanced Manufacturing industries.
“The immense amount of data being generated by the industrial internet of things (IIoT) is propelling the adoption of edge, fog, and cloud computing capabilities in Industry 4.0. Custom hardware and software solutions like connected clouds, distributed clouds, distributed compute and storage, hybrid computing, low code development platforms, microservices, mobile computing, and multi-access edge computing are shaping up this industry 4.0 trend.”
Cybersecurity
Due to more connected devices thanks to IIoT, as well as the covid-inspired transition to more remote working conditions, there is an increased risk of exposure to many more vulnerabilities and thus need for security and privacy are higher than ever.

